Understanding Bluetooth Security: A Hands-On Guide
Demystifying wireless vulnerabilities and how security professionals protect against them
Why Bluetooth Security Matters
In our connected world, billions of devices communicate wirelessly through Bluetooth—from wireless headphones to medical devices and vehicles. While this makes life easier, insecure configurations can expose users to risks if left unprotected.
This article explores how security professionals identify and address Bluetooth vulnerabilities using legitimate, ethical tools — helping manufacturers build safer products and consumers stay informed.

How Bluetooth Works (Simply Explained)
Think of Bluetooth like invisible walkie-talkies between your devices. When your phone pairs with a speaker, they create a temporary encrypted channel to exchange data. Just like locks, some configurations can be stronger than others.

The Security Professional's Toolkit
Ethical security researchers use specialized systems like Kali Linux — a distribution equipped with tools for lawful testing and vulnerability assessment in controlled environments.
Finding Bluetooth Devices (Discovery Phase)
Before any testing, professionals map the environment to see which devices are discoverable. This step is comparable to checking which Wi-Fi networks are visible nearby. It's purely observational — no interaction or connection is made.
# Enable Bluetooth adapter
sudo hciconfig hci0 up
# Search for standard Bluetooth devices
sudo hcitool scan
# Search for low-energy devices (modern gadgets)
sudo hcitool lescan
Gathering Device Information
Once discoverable devices are identified, researchers record metadata like device type, supported services, and signal strength. This helps classify devices and identify those using outdated security protocols.
# Get detailed device information
sudo hcitool info [MAC_ADDRESS]
# Check what services the device offers
sdptool browse [MAC_ADDRESS]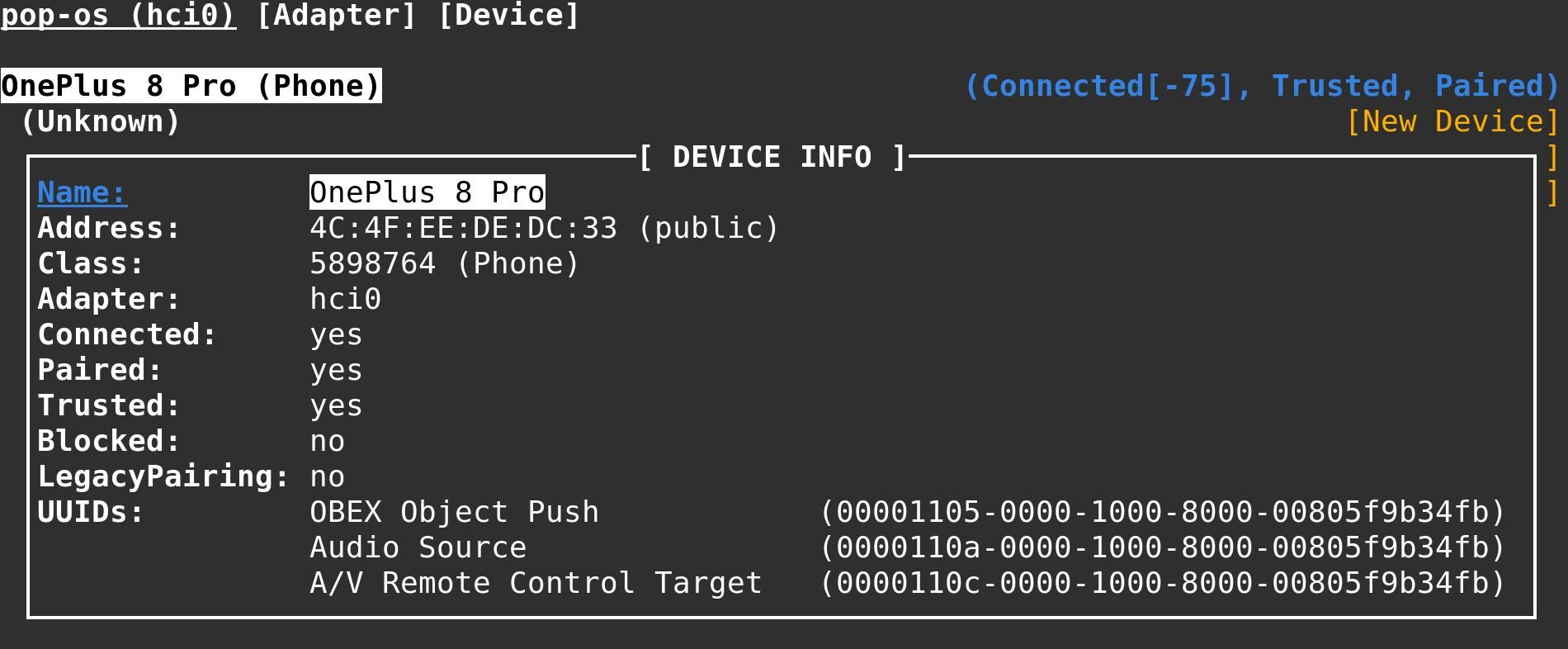
Advanced Testing (In Authorized Labs)
In authorized security labs, researchers use visualization tools to monitor Bluetooth communications, analyze protocol behavior, and identify potential weaknesses that vendors can fix. This is done ethically under written permission and clear scope.
# Start comprehensive Bluetooth recon tool
sudo bettercap -iface hci0
> ble.recon on
Analyzing Encrypted Communications
Researchers sometimes study how well encryption mechanisms are implemented by devices they own or are authorized to test. This ensures newer devices meet modern encryption standards and helps patch weak cryptographic implementations.
# Capture Bluetooth traffic
sudo ubertooth-btle -f -c capture.pcap
# Analyze encryption with CrackLe
crackle -i capture.pcap
Protecting Yourself from Bluetooth Risks
- Keep devices updated: Install firmware and OS updates promptly.
- Turn off discoverability: Only make your device visible while pairing.
- Use secure authentication: Avoid default or weak pairing codes.
- Audit connections: Regularly remove unused paired devices.
Final Thoughts
Bluetooth security is a shared responsibility between users, manufacturers, and researchers. When vulnerabilities are found and reported ethically, they make the entire ecosystem stronger and safer.
As consumers, staying aware, applying updates, and following best practices are the best defenses against wireless threats.





0 Comments